Home / Building Structures & Components / Roofing
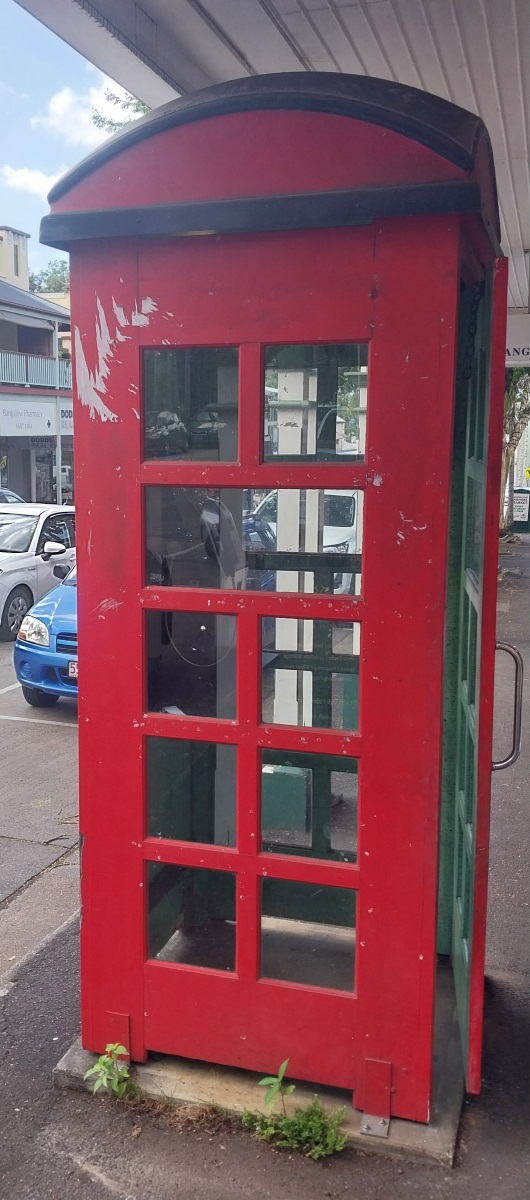
Telephone booth roofs
Description
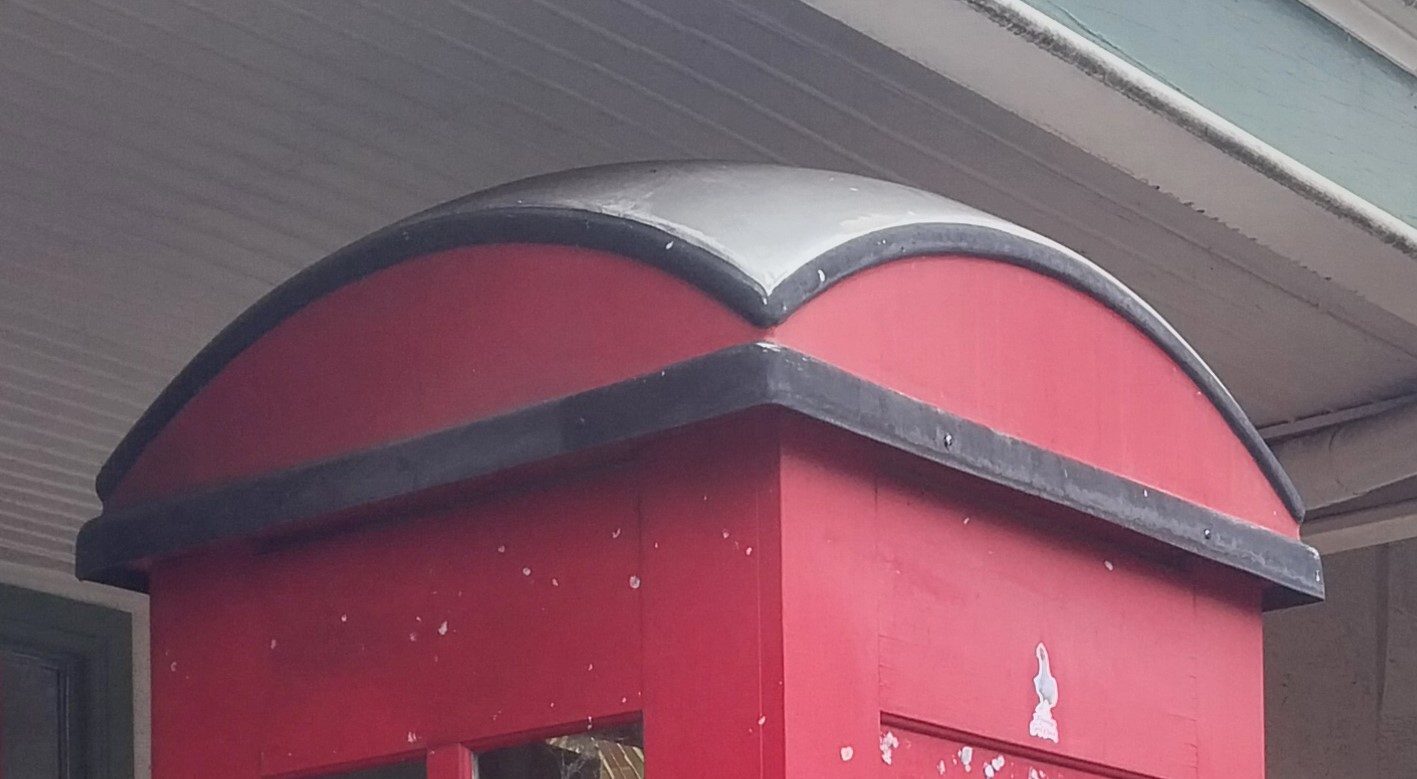
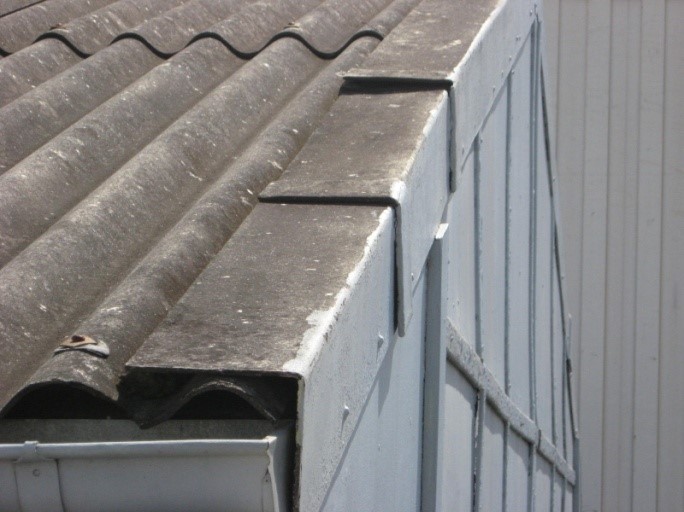
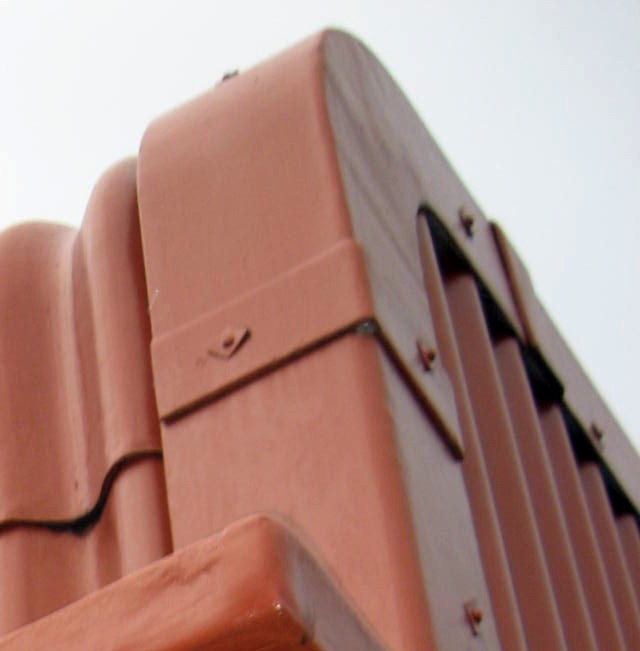
Moulded AC roof designed to withstand strong weathering.
Manufactured in Australia for former
Postmaster-General’s Department (PMG).
ACM content appears isolated to rounded design, rather than including pyramid, pagoda or other designs.
Also known as public telephone cabinets. Up until the aluminium booths were introduced in Australia in the 1960s, there were many different designs used by the PMG, often with a tailored design to suit varied weather environments around Australia.
Of these, it is apparent the use of AC was restricted to two designs, both with a dome shaped roof:
- The Kiosk No. 3, which was a steel cabinet, produced in small numbers in the early 1940s, and
- The Modified Standard Cabinet (aka Louvre Glazed cabinet when fitted with glass louvres), a wooden design produced in the 1950s-60s.
These are of demand for ‘retro’ novelty value and so subject to renovation for re-sale or use.
Brands/products
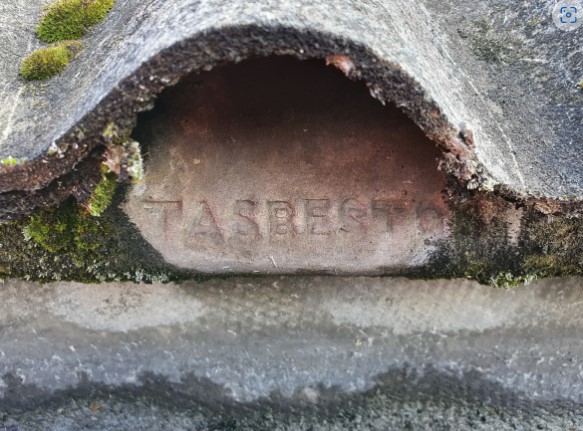
- Tasbestos
- Fibrolite
Years of production/use
1940-1960s
Residential uses
Current collectors
Industrial uses
Novelty phone box in publicly accessible areas
Be aware
Disturbance of fibres during renovation.
Will likely deteriorate if left unmaintained and subject to weathering.