Description
Small access points that house telecommunication cables and jointing equipment. Provide protection to cables/equipment from damage and access for maintenance. Designed for reach-in access rather than climbing access.
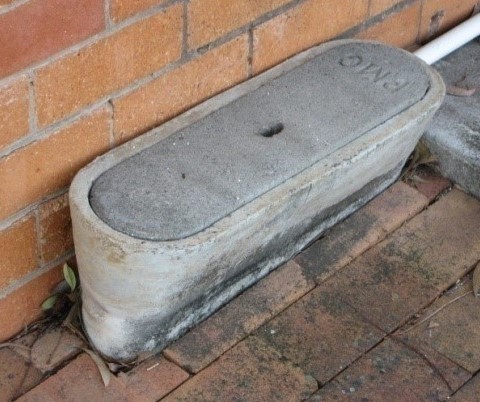
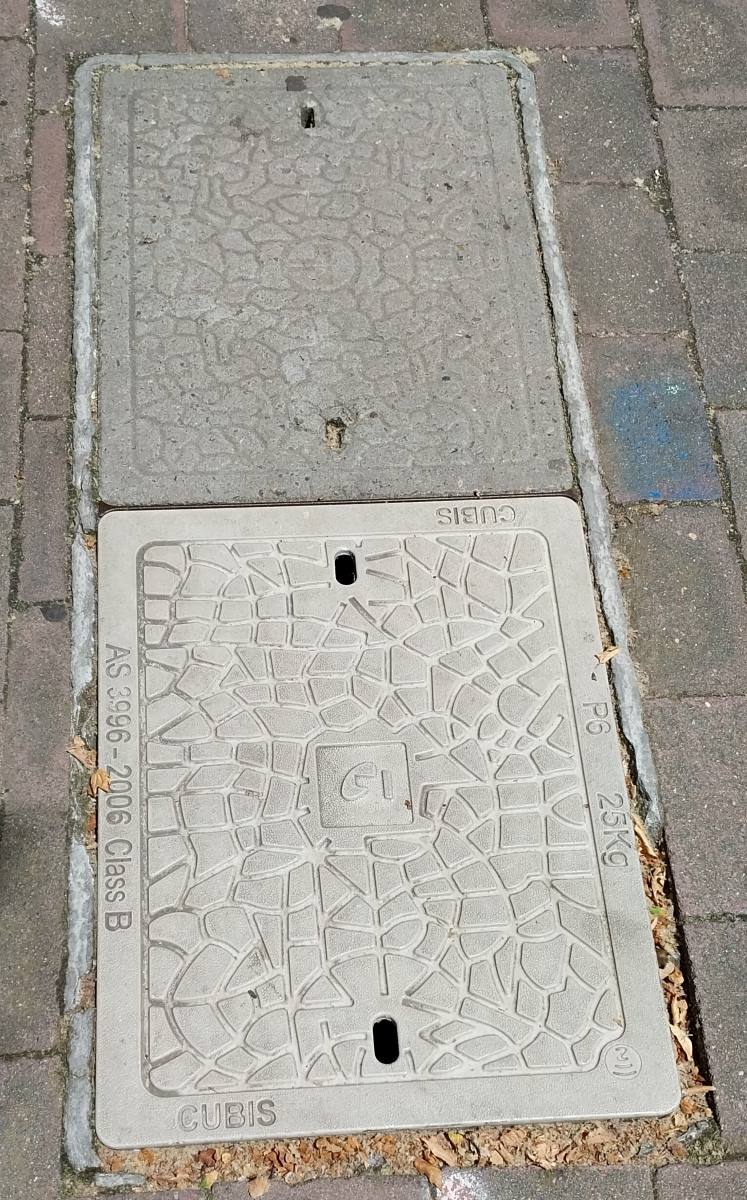
The pit is a moulded semi-enclosed housing usually inserted into ground with a removable lid inserted into the top at surface level. May be sited in publicly accessible soil, tarmac, verges, pathways, or on private property.
ACM pits were produced in a few different top surface shapes:
- The smaller pits are (1m length) round ended with straight long edges or rectangular with rounded corners.
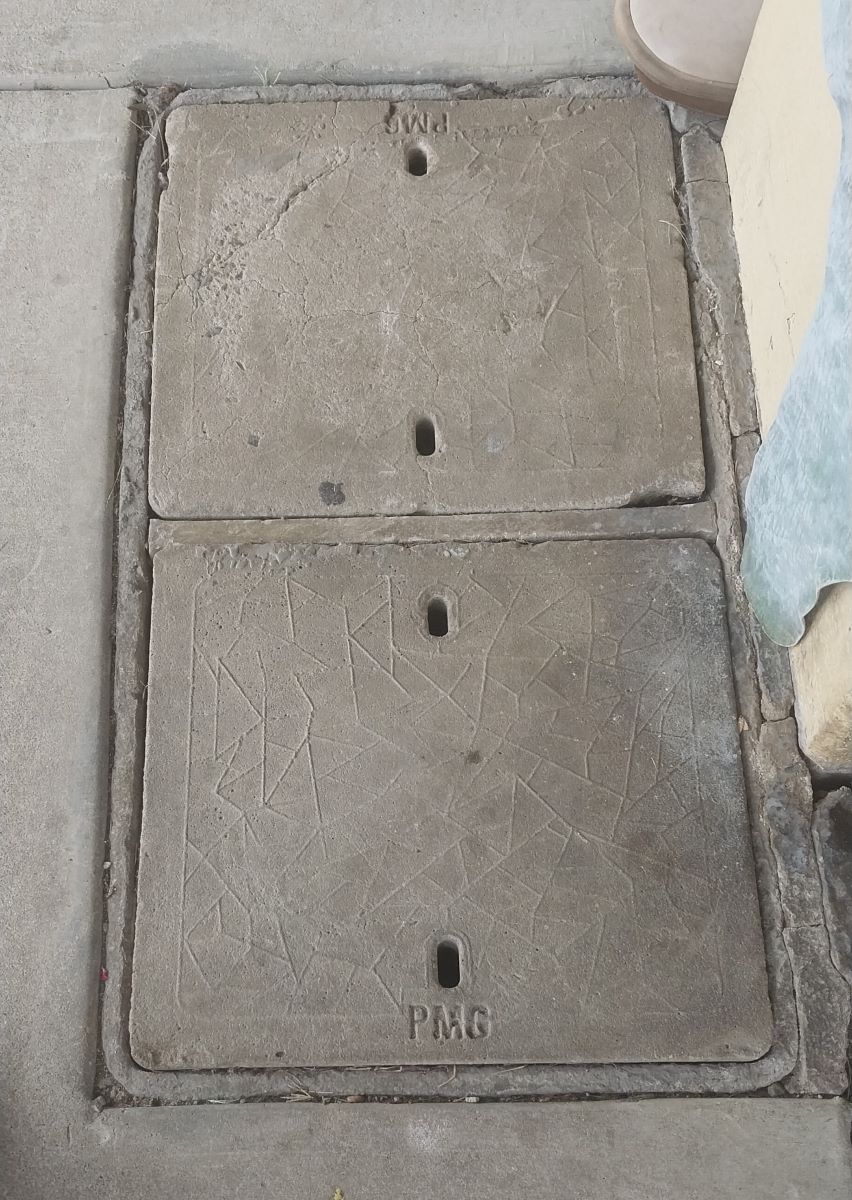
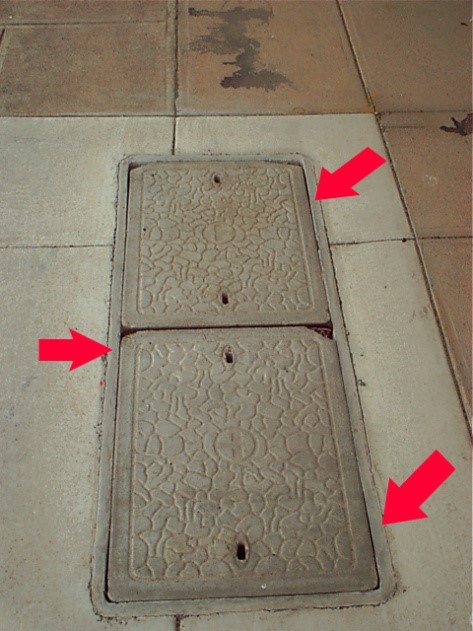
- The slightly larger are rectangular with rounded corners (650x400mm). These may be laid in twos over a single pit, usually end to end.
- The siding of the ACM pit is usually exposed at surface surrounding the lid.
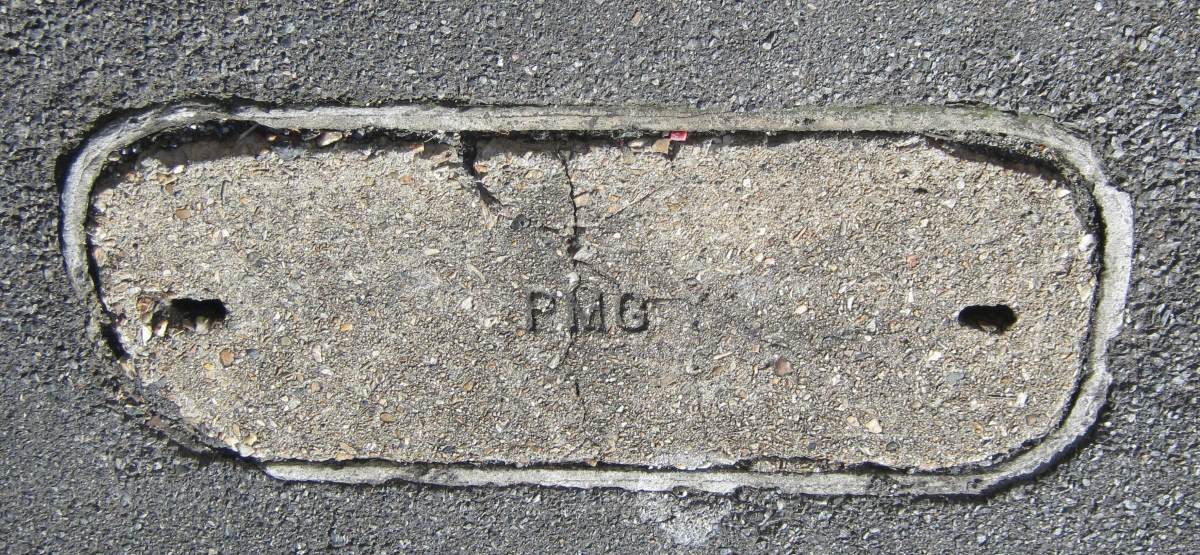
- The lids are pre-cast concrete with one or two holes to provide access for lifting tools.
- The former Telecom Australia or PMG symbol is cast into the top.
- Distortion of shape may occur over time when in ground.
Manufactured by all the major AC manufacturers for the former Postmaster-General’s Department (PMG) and later Telecom Australia between the 1930s and the 1980s. Concrete cast pits were also installed throughout this period, as well as polyethylene moulded pits from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. During the 1980s cellulose cement moulded pits were installed at the same time as the ACM pits were being phased out. Telstra references both ACM and cellulose material as fibre cement (Telstra contractor guidance 2018).
Brands/products
- James Hardie
- Wunderlich
- Goliath Portland cement (Tasbestos)
- Asbestolite
- CSR-Wunderlich Building Materials (1970s)
Years of production/use
Late 1930s to 1980s
Pits are not manholes, which are larger and are of square or rectangular shape, with multiple metal or metal-lined lids. Constructed of steel and/or concrete. Older AC conduits housing cables may still be connected to larger manholes, which, if damaged or disturbed, may account for AC debris inside manhole area.
Refer: Asbestos cement conduit for electrical and telecommunication cables.
Residential uses
n/a
Industrial uses
As described
Be aware
Exposed AC surfaces subject to weathering likely deteriorate over time exposing fibre bundles.
Telstra applies the presumptive test that all non-plastic pits are to be treated as ACM. Older suburbs adjacent to modern CBD areas are likely to have a larger number of pits that are likely to contain ACM (Telstra contractor guidance 2018). A removal/replacement program has been under way in recent years.
Pits must not be opened unless the person is trained as a Telstra accredited plant locator, an authorised contractor, or a before-you-dig certified locating professional.
To contact Telstra with asbestos related enquiries, phone 1800 067 225.